We offer a combination of corrective bracing and vacuum bell therapy to treat pectus deformities such as pectus carinatum and pectus excavatum, in tandem with specialist breathing and Yoga exercise programmes to achieve pectus correction.
For patients who want to avoid surgery, conservative chest bracing treatment can be a great way to achieve a flatter chest, but often, patients are unsure of what treatment involves.
During their initial consultation, our pectus clinicians are often asked common questions about the nature of treatment and which lifestyle changes they can make for bracing to be most successful. For some patients, it’s learning what life will be like while wearing a chest brace and if it will infringe upon their day-to-day lifestyle.
Below you can see a series of videos that deal with some of our most frequently asked questions about pectus deformity treatment, with LOC director and pectus specialist, Sam Walmsley, answering them.
We hope these videos will prove a useful source of information as well as comfort for people considering bracing treatment as an alternative to surgery.
If you have any more questions or would like to make an appointment to talk through treatment, you can arrange a free online consultation via Skype, Facetime or Zoom.
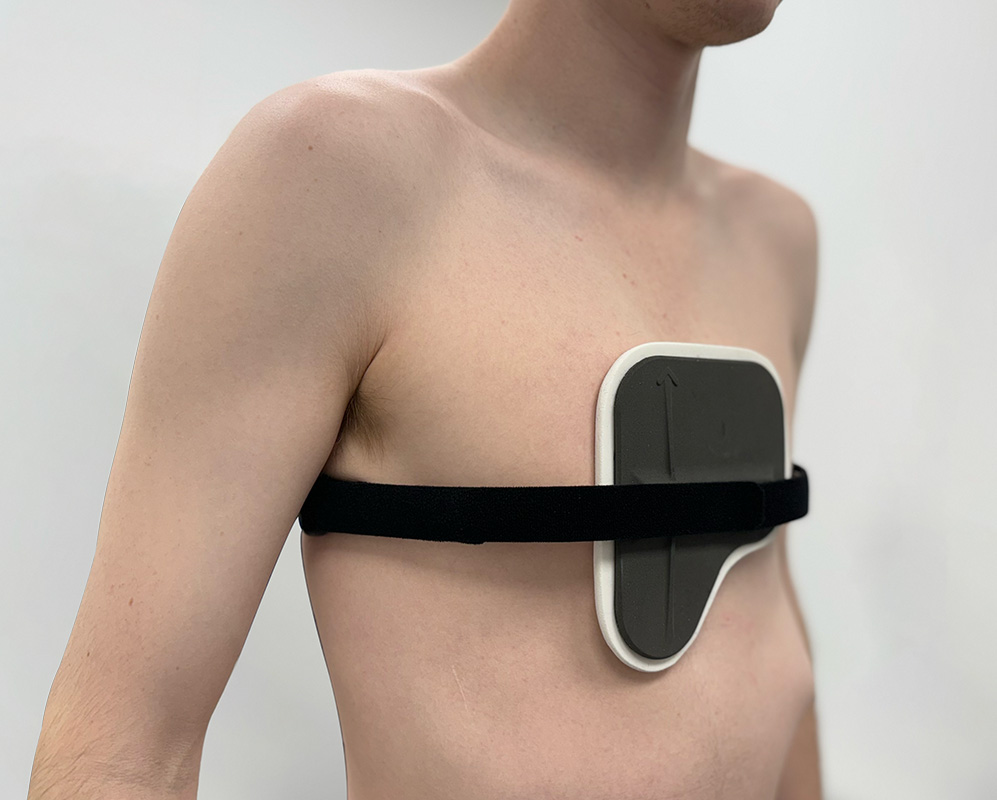
Bespoke Dynamic Chest Compressor brace for pectus carinatum treatment
This depends on several factors; the position of the chest wall deformity, its severity, the flexibility of the chest, the kind of results wanting to be achieved and the age of the person undergoing treatment for pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum.
Early adolescence (roughly between the ages of 12-16 years old) – is an optimum age to start treatment, given that the chest is still maturing, and flexible, permanent correction is more easily achievable. Once bracing treatment is complete and a patient has stopped growing, the deformity will not return. For younger pectus patients, conservative bracing is used to keep a deformity from worsening and can help them to avoid surgery in later life.
For older pectus patients (between the ages of 20 to 30) results can be harder to achieve, as the costal cartilage hardens into the bone as a person matures. Over the years we have successfully treated many adults for both pectus excavatum and pectus carinatum and active adults with flexible chests can expect good results.
Again, this hugely depends on what a patient wants to achieve from treatment; whether that’s avoidance of surgery, improvement in the appearance of the chest shape, reduction in rib flaring etc.
All these goals are taken into consideration during your first consultation. While there are no serious health risks of having pectus carinatum or excavatum – beyond the cosmetic – for many patients and parents, treatment outcomes involve improving confidence and self-esteem.
During our 2018 Pectus Patient Survey, 92% of pectus carinatum patients surveyed said that treatment had a ‘major improvement’ or ‘an improvement’ on their social life.
You can read the results of our 2018 Pectus Patient Survey and quality of life questionnaire here.
Regular reviews are part of the treatment programme, preferably at our clinic with one of our specialist orthotists, or via virtual consultations.
The number of appointments needed will vary from patient to patient but as a general rule, younger pectus patients who are growing at a faster rate will need to be seen more regularly for check-up appointments. This is to ensure that the brace fits well and is guiding the chest into the correct position as growth spurts occur. For other patients, this can be scaled back according to their individual needs and demands.
Regular appointments are beneficial for assessing progress, checking for signs of rubbing and determining whether another brace is needed. Appointments are also good for checking patient compliance to brace wearing and the breathing and exercise programme.
We always advise coming in for appointments whenever you have any concerns about the brace or treatment programme, especially if a brace is rubbing or not fitting correctly. At the London Orthotic Consultancy, we have treated numerous international patients that have benefitted from specially designed braces that leave room to accommodate for growth and that can be adjusted remotely. Follow-up appointments for international patients are conducted via Facetime or Zoom.
At this consultation, one of LOC’s specialist clinicians will examine your chest and also your general posture. Your alignment from head to toe will be checked for signs of asymmetry. They will test the flexibility of your chest and determine the structural type of pectus you have.
Please note that patients under the age of 18 must be accompanied by a parent or legal guardian for all appointments.
If you want to proceed with treatment and the clinician believes that your chest shape will respond using the Dynamic Remodelling method, the clinician will take a series of photographs and 3D scans of your chest shape. Further appointments for casting and then fitting of your brace will be made. Both of these will be about an hour in length.
This is a very common concern for patients considering treatment; in general, the Dynamic Chest Compressor brace is easy to conceal if you are wearing a loose-fitting shirt for school or work.
If you are wearing two chest braces – one for the main deformity and the other for rib flaring – then this may be more noticeable, especially under a t-shirt. Normally loose-fitting clothing will conceal the brace, though it’s likely it will be seen through tight-fitting clothes.
It is really important to continue exercising while going through bracing treatment. Exercise is fundamental to keeping the chest wall flexible. Deep breathing exercises allow the lungs to expand against the chest wall, pushing it outwards.
Exercising with the brace on in the later stages of treatment can also make the chest correction more stable and permanent.
Swimming is one of the best forms of exercise to complement bracing treatment, as the body positions required to swim imitate the resistance band training designed to stretch the chest and increase its flexibility. Some swimming strokes are better for this than others, please check with your clinician. The brace should always be removed for contact sports and for swimming.
For most patients, one brace is often all that is needed to achieve a desired level of correction. They are each designed to last the duration of treatment and accommodate any growth that may occur in that time.
Some patients have benefitted from having two braces – one to treat the main deformity and the other to treat rib flaring. For some pectus excavatum patients, having a brace apply pressure to the ribs – in addition to vacuum bell therapy – can greatly reduce the appearance of the depressed sternum area of the chest, forcing it upwards and outwards into a more corrective position.
If you are worried about your chest shape, or your child’s chest shape, then get in touch for a free virtual consultation with one of our pectus specialists who can assess their chest and discuss treatment options. We are always happy to communicate with local GPs, thoracic surgeons and consultants if a patient approaches us for bracing treatment after considering other options.
The Dynamic Chest Compressor is a custom made orthosis that is designed for an individual’s anatomy and to specifically treat their particular type of deformity. Its objective is to apply pressure over areas of the skeleton to remodel chest and rib bones.
This concept is called Wolfe’s Law and is used in dentistry where braces are used to remodel the jaw. There are two main areas where we apply this pressure: centrally on the sternum and if the ribs begin to flare, either side at the bottom of the rib cage.
The Vacuum Bell was invented by Eckart Klobe, a graduate in Chemical Engineering; it has been used successfully in the treatment of pectus excavatum by a number of German, Austrian and Swiss clinics over the last decade.
The Bell works by using a silicone cup and a vacuum pump to create an area of low pressure over the sunken part of the chest. LOC’s advice is to wear the cup immediately after the completion of the daily exercise programme. This is when the chest should be at its most flexible and will maximise the effect of the correctional forces of the Bell.